
Comprehensive Literacy for Multilingual Learner/English Learner students (ML/ELs) is an all-encompassing approach that leverages the linguistic and social-cultural dimensions of bilingualism and recognizes the complexities of literacies in multiple contexts. It recognizes the need for explicit, systematic, and direct instruction capitalizing on cross-linguistic resources and considers the unique needs of English Learners such as the development of the second language through integrated and designated English Language Development (ELD) instruction for the successful attainment of academic language and content knowledge in English. At the same time, the approach aims at fostering a love of reading by attending to the whole child, including their likes, dislikes, motivations, interests, and background knowledge (Gambrell et al., 2011; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2017; Escamilla et al., 2022).
Specific elements for a Comprehensive Literacy for ML/EL students include:
|
As new literacy initiatives emerge and develop it is essential that local and state policymakers’ use the research on second language literacy to create and implement policies that respond to the strengths and needs of ML/EL students. Language and literacy initiatives should offer program options that leverage primary language instruction and the various approaches to multilingualism. An example of state policy documents that can guide the implementation of a Comprehensive Literacy program for ML/ELs is the current California’s ELA/ELD Framework, California 2030, and the California English Learner Roadmap policies that reflect the state’s strong commitment to a multilingual vision for education.
The California ELA/ELD Framework (2014), the guiding document for the implementation of Language Arts and ELD instruction in the state, has incorporated this comprehensive literacy approach by placing integration, motivation, and engagement as the context in which instruction should occur. The Framework also stipulates that English Learners’ needs must be considered within five crosscutting themes of the ELA and ELD Standards. These themes are 1) Meaning Making, 2) Language Development, 3) Effective Expression, 4) Content Knowledge, and 5) Foundational Skills. Together they build a robust and comprehensive instructional program for all students, especially ELs.
The CA EL Roadmap Policy identifies 4 main principles and related subthemes to consider when creating plans and programs for English Learners (CDE, 2018). These are 1) Assets-Oriented and Needs Responsive Schools, 2) Intellectual Quality of Instruction and Meaningful Access, 3) System Conditions that Support Effectiveness, 4) Alignment and Articulation Within and Across Systems.
Furthermore, four decades of research focusing on second language literacy development and instruction have identified components of effective literacy education for English learners that anchor California’s EL policies, the ELA/ELD framework and support a comprehensive literacy approach (August & Shanahan, 2006; Genesee et al, 2006; Piazza, S. V., Rao, S., & Protacio, M. S., 2015)
CEEL Engagement in EL Advocacy
CEEL engages with a number of organizations, programs, and events that are striving to ensure that policy, programs, and practices address the unique needs of English Learners and align to a comprehensive literacy approach.
- California Association for Bilingual Education
- Californians Together
- National Committee for Effective Literacy
- California Committee for Effective Literacy
- UnboundEd
Read more about CEEL’s leadership, key resources, and recommendations in the links below.
- CCEL brief
- EL Roadmap Policy Brief, Advancing Coherence
- Examining the English Learner Policy Ecology
- Essential Elements of Effective Practices for English Learners
- Literacy Resources for Educators and Families
- Reading League SUMMIT Joint Statement
- Tierney & Pearson’s Executive Summary of Fact-checking the Science of Reading
- Toward Comprehensive Effective Literacy Policy and Instruction for English Learner/Emergent Bilingual Students

CCEL Brief
Guidelines for effective literacy education to support English Learner and Emergent Bilingual students in California.

EL Roadmap Policy Brief, Advancing Coherence
This brief recommends aligning teacher preparation in IHEs with TK-12 policies, using resources like the California English Learner Roadmap Toolkit to better support English Learners.

Examining the English Learner Policy Ecology
Explores how two California districts address English-language development (ELD) for secondary English learners (ELs).

Essential Elements of Effective Practices for English Learners
Highlights the need for high-quality teacher preparation and professional development to improve English Learners' success.
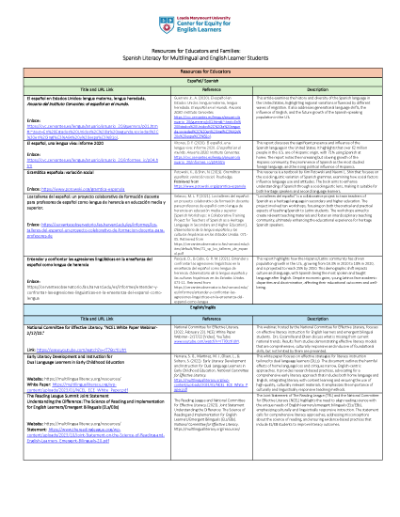
Literacy Resources for Educators and Families
Resources and links related to Spanish Literacy for Multilingual and English Learner Students.
-400x517.png)
Reading League SUMMIT Joint Statement
Joint statement on the implementation of the Science of Reading as it pertains to English Learners/Emergent Bilinguals (ELs/EBs)
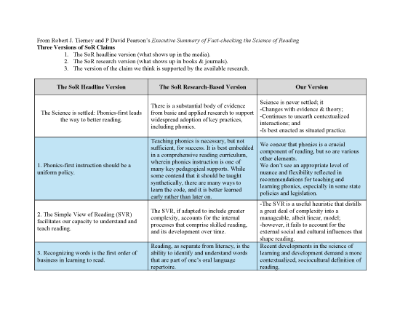
Tierney & Pearson’s Executive Summary of Fact-checking the Science of Reading
Identifying the analysis of the three versions of the Science of Reading Claims.

Toward Comprehensive Effective Literacy Policy and Instruction for English Learner/Emergent Bilingual Students
Discusses and analyzes literary approaches and the one-size fits all model.

Dual Language/Multilingual Programs
Provides information from experts in the field on Dual Language Programs and first language literacy.
From May CDE MSD BCN Meeting
- CA Statewide Literacy Roadmap: BCN May 2024 Literacy Roadmap PPT
- BCN May 2024 Literacy Roadmap Outline
- BCN May 2024 Screening for Risk of Reading Difficulties
References
August, D., & Shanahan, T. (Eds.). (2006). Developing literacy in second-language learners: Report of the National Literacy Panel on Language-Minority Children and Youth. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Escamilla, K, Olsen, L. and Slavick, J. (2022). Toward Comprehensive Effective Literacy Policy and Instruction for English Learner/Emergent Bilingual Students [White paper]. The National Committee for Effective Literacy. 21018 NCEL Effective Literacy White Paper FINAL.indd
Gambrell, L.B., Malloy, J.A., Janice F., and Mazzoni, S.A. (2011). Evidenced-based best practices in comprehensive literacy instruction. In Lesley Mandel Morrow, Linda B. Gambrell (Eds.), Best Practices in Literacy Instruction (pp.11-36). New York: Guilford Press.
Genesee, F., Lindholm-Leary, K., Saunders, W. M., & Christian, D. (Eds.). (2006). Educating English language learners: A synthesis of research evidence. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511499913
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (2017). Promoting the Educational Success of Children and Youth Learning English: Promising Futures. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. https://psycnet.apa.org/doi/10.1017/CBO9780511499913
Piazza, S. V., Rao, S., Protacio, M. (2015). Converging Recommendations for Culturally Responsive Literacy Practices: Students with Learning Disabilities, English Language Learners, and Socioculturally Diverse Learners. International Journal of Multicultural Education, v17 n3 p1-20.